Navigating the financial landscape often involves understanding a range of terminologies and procedures, two of the most common being hard and soft credit checks. Especially in the UK, where credit scores play an important role in a lender’s financial decisions, knowing the difference is crucial.
Soft Credit Checks
Definition:
A soft credit check, frequently referred to as a ‘soft search’, offers a high-level view of your credit file. It doesn’t dig deep but provides enough information to give a preliminary understanding of your credit standing.
Effects on Your Credit Score:
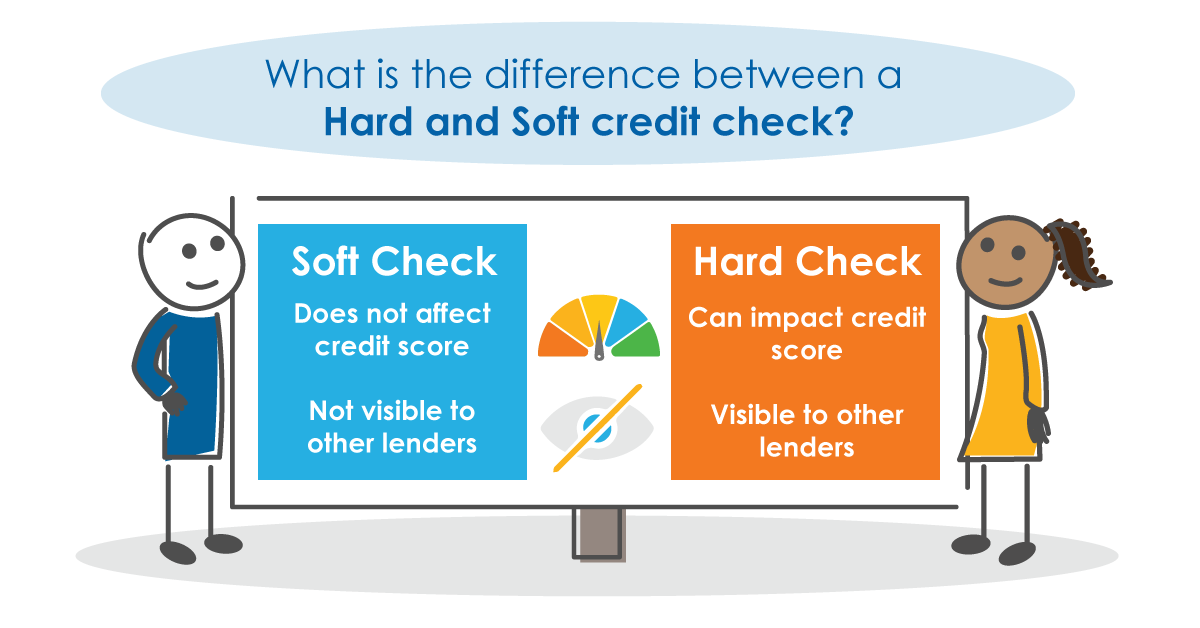
One of the main features of a soft check is its non-invasive nature. It leaves no lasting impression on your credit file, meaning future lenders won’t see soft search footprints. Consequently, you can have multiple soft checks without them reducing your credit score or affecting any future credit applications.
Typical Scenarios for Soft Checks:
- Preliminary rate offers: Before offering an interest rate on a loan or credit card, many providers run soft checks to give an indicative rate.
- Eligibility checkers: Many online tools allow you to check your eligibility for specific financial products without affecting your score. These use soft searches.
- Annual credit report checks: In the UK, you’re entitled to check your credit report yearly. Doing so involves a soft check.
- Account management: Existing lenders might run periodic soft searches to review the status of an account or customer.
Hard Credit Checks
Definition:
A hard credit check, or ‘hard search’, is a thorough review of your credit file. It gives a complete picture of your credit history, helping lenders assess the risk associated with lending to you.
Effects on Your Credit Score:
- Short-term impact: A hard search can cause a slight drop in your credit score. This is temporary, but multiple hard checks in quick succession can compound this effect, causing a more noticeable decrease.
- Visibility: Hard searches remain on your credit report for 12 months. These footprints can be seen by other lenders. If they see multiple recent hard checks, they might interpret this as a sign that you’re in financial trouble or are credit-hungry, potentially making them more hesitant to approve your application.
Typical Scenarios for Hard Checks:
- Loan applications: Whether it’s a personal loan, mortgage, or car finance, lenders will typically conduct a hard search.
- Credit card applications: When you apply for a new credit card, expect a hard search.
- Mobile phone contracts: Many providers conduct hard checks before agreeing to a monthly contract.
- Rental applications: Some landlords or letting agencies might choose to do a hard search before renting out a property, especially if the rent is high or the rental period is long.
Key Differences At A Glance:
- Impact on credit score: Soft checks have no effect, while hard checks can temporarily decrease your score.
- Visibility: Soft checks are invisible to future lenders; hard checks leave a footprint visible for 12 months.
- Purpose: Soft checks provide a snapshot, often used for preliminary offers or eligibility checkers. Hard checks offer a comprehensive view, used for final lending decisions
Conclusion
While both soft and hard credit checks aim to assess an individual’s creditworthiness, they differ significantly in their impact and visibility on a credit file. In the UK’s financial ecosystem, understanding these differences is essential. Whether you’re looking to rent a flat, take out a loan, or simply keep tabs on your creditworthiness, it’s crucial to know the type of search you’re consenting to and its implications.



